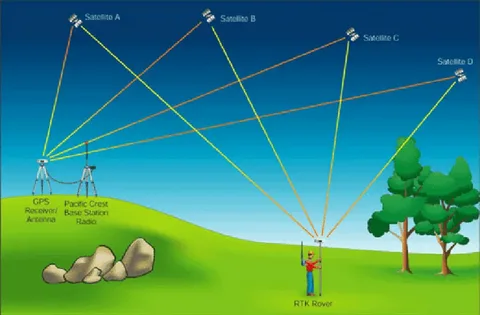
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) have revolutionized navigation, positioning, and timing services across the globe. With the advent of multi-constellation GNSS system, the accuracy, reliability, and coverage of satellite-based navigation have reached unprecedented levels. In this article, we explore the advantages and applications of multi-constellation GNSS systems, highlighting why they are becoming the standard for modern navigation solutions.
Understanding Multi-Constellation GNSS Systems
A multi-constellation GNSS system refers to a navigation setup that leverages signals from multiple satellite constellations, such as GPS (USA), GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (EU), and BeiDou (China). Unlike single-constellation systems, which rely on satellites from only one provider, multi-constellation systems can access a larger number of satellites, resulting in better accuracy and signal reliability.
Advantages of Multi-Constellation GNSS Systems
1. Enhanced Accuracy
By combining signals from multiple constellations, multi-constellation GNSS systems can significantly reduce positioning errors caused by atmospheric interference, satellite geometry limitations, or signal obstructions. This ensures centimeter-to-meter-level precision in both urban and remote areas.
2. Improved Reliability and Availability
Relying on a single GNSS constellation can be risky, especially in environments with signal blockage, such as urban canyons or dense forests. Multi-constellation systems increase satellite visibility, ensuring continuous navigation even if some satellites are temporarily unavailable.
3. Faster Time-to-First-Fix (TTFF)
A larger pool of available satellites allows multi-constellation GNSS systems to acquire signals more quickly, resulting in faster initialization times for devices requiring positioning services.
4. Robustness Against Interference
Using multiple constellations makes the system more resilient to signal interference or jamming, enhancing safety-critical applications in aviation, maritime navigation, and autonomous systems.
Applications of Multi-Constellation GNSS Systems
1. Aviation and Maritime Navigation
Airplanes and ships benefit from multi-constellation GNSS systems through enhanced accuracy and reliability, which are crucial for route planning, collision avoidance, and precision landings or docking.
2. Autonomous Vehicles and Robotics
Self-driving cars, drones, and industrial robots rely on precise positioning data. Multi-constellation GNSS systems enable these technologies to navigate safely, even in challenging environments like urban centers or remote areas.
3. Surveying and Mapping
Surveyors and geospatial professionals use multi-constellation GNSS systems to achieve high-precision measurements in land surveying, construction, and geographic information systems (GIS).
4. Agriculture
Modern precision agriculture uses GNSS for planting, harvesting, and field monitoring. Multi-constellation systems ensure accuracy even in large fields or regions with limited satellite visibility.
5. Disaster Management and Emergency Services
During natural disasters or emergencies, reliable positioning data is critical for rescue operations and resource deployment. Multi-constellation GNSS systems improve location accuracy for responders in challenging environments.
Conclusion
The adoption of multi-constellation GNSS systems is transforming the way we approach navigation, positioning, and timing across multiple industries. With their enhanced accuracy, reliability, and robustness, these systems are not only ideal for everyday applications but also critical for safety-sensitive and high-precision operations. As more satellite constellations become operational, the capabilities of multi-constellation GNSS systems will continue to expand, driving innovation and efficiency in global navigation.